FDA records indicate that there are no current recalls for this drug.
Are you a medical professional?
Trending Topics
Baman 40 Recall
Get an alert when a recall is issued.
Questions & Answers
Side Effects & Adverse Reactions
There is currently no warning information available for this product. We apologize for any inconvenience.
Legal Issues
There is currently no legal information available for this drug.
FDA Safety Alerts
There are currently no FDA safety alerts available for this drug.
Manufacturer Warnings
There is currently no manufacturer warning information available for this drug.
FDA Labeling Changes
There are currently no FDA labeling changes available for this drug.
Uses
Levalbuterol inhalation solution USP (concentrate) is indicated for the treatment or prevention of bronchospasm in adults, adolescents, and children 6 years of age and older with reversible obstructive airway disease.
History
There is currently no drug history available for this drug.
Other Information
Levalbuterol inhalation solution USP (concentrate) is a sterile, clear, colorless, preservative-free solution of the hydrochloride salt of levalbuterol, the (R)-enantiomer of the drug substance racemic albuterol. Levalbuterol hydrochloride, USP is a relatively selective beta2-adrenergic receptor agonist [see Clinical Pharmacology (12)]. The chemical name for levalbuterol hydrochloride, USP is (R)-α1-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]methyl]-4-hydroxy-1,3-benzenedimethanol hydrochloride, and its established chemical structure is as follows:
The molecular weight of levalbuterol hydrochloride, USP is 275.8, and its empirical formula is C13H21NO3•HCl. It is a white to off-white, crystalline solid, with a melting point of approximately 188°C and is soluble in water and slightly soluble in ethanol.
Levalbuterol hydrochloride, USP is the USAN modified name for (R)-albuterol hydrochloride in the United States.
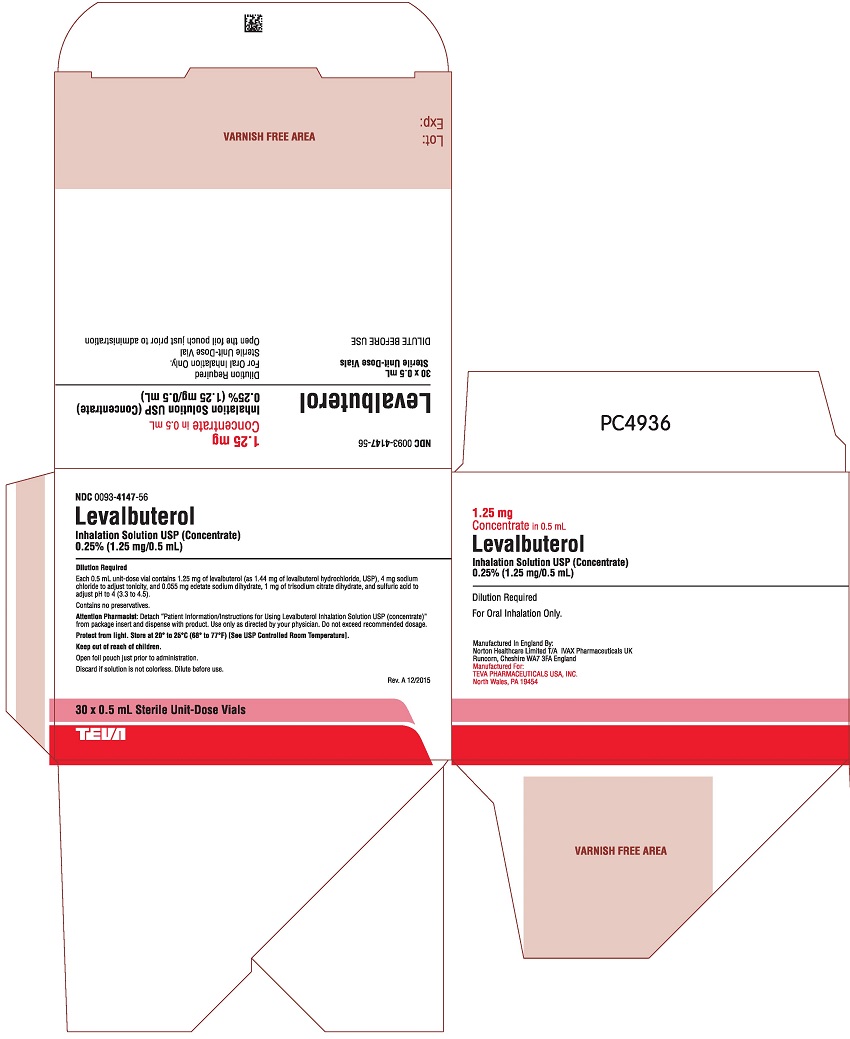
Levalbuterol inhalation solution USP (concentrate) is supplied in 0.5 mL unit-dose vials that must be diluted with normal saline before administration by nebulization. Each 0.5 mL unit-dose vial contains 1.25 mg of levalbuterol (as 1.44 mg of levalbuterol hydrochloride, USP), 4 mg sodium chloride to adjust tonicity, and 0.055 mg edetate sodium dihydrate, 1 mg of trisodium citrate dihydrate, and sulfuric acid to adjust pH to 4 (3.3 to 4.5).
Sources
Baman 40 Manufacturers
-
Paramesh Banerji Life Sciences Llc
![Baman 40 (Number 50) (Chelidonium Majus, Aethusa Cynapium) Pellet [Paramesh Banerji Life Sciences Llc]](/wp-content/themes/bootstrap/assets/img/loading2.gif)
Baman 40 | Teva Pharmaceuticals Usa Inc
![Baman 40 (Number 50) (Chelidonium Majus, Aethusa Cynapium) Pellet [Paramesh Banerji Life Sciences Llc] Baman 40 (Number 50) (Chelidonium Majus, Aethusa Cynapium) Pellet [Paramesh Banerji Life Sciences Llc]](/wp-content/themes/bootstrap/assets/img/loading2.gif)
Levalbuterol inhalation solution (concentrate) is for oral inhalation only. Dilute with sterile normal saline before administration. Administer by nebulization using a standard jet nebulizer (with a face mask or mouthpiece) connected to an air compressor. Do not exceed recommended dose. For dosages less than 1.25 mg, the non-concentrate (i.e., levalbuterol inhalation solution, 3mL) formulation must be used.
Children 6 to 11 years old: The recommended dosage of levalbuterol inhalation solution for patients 6 to 11 years old is 0.31 mg administered three times a day, by nebulization. Routine dosing should not exceed 0.63 mg three times a day.
Adults and Adolescents ≥ 12 years old: The recommended starting dosage of levalbuterol inhalation solution for patients 12 years of age and older is 0.63 mg administered three times a day, every 6 to 8 hours, by nebulization.
Patients 12 years of age and older with more severe asthma or patients who do not respond adequately to a dose of 0.63 mg of levalbuterol inhalation solution may benefit from a dosage of 1.25 mg three times a day.
Patients receiving the highest dose of levalbuterol inhalation solution should be monitored closely for adverse systemic effects, and the risks of such effects should be balanced against the potential for improved efficacy.
The use of levalbuterol inhalation solution can be continued as medically indicated to help control recurring bouts of bronchospasm. During this time, most patients gain optimal benefit from regular use of the inhalation solution.
If a previously effective dosage regimen fails to provide the usual response this may be a marker of destabilization of asthma and requires reevaluation of the patient and the treatment regimen, giving special consideration to the possible need for anti-inflammatory treatment, e.g., corticosteroids.
The drug compatibility (physical and chemical), efficacy, and safety of levalbuterol inhalation solution when mixed with other drugs in a nebulizer have not been established.
The safety and efficacy of levalbuterol inhalation solution have been established in clinical trials when administered using the PARI LC Jet™ and PARI LC Plus™ nebulizers, and the PARI Master® Dura-Neb® 2000 and Dura-Neb® 3000 compressors. The safety and efficacy of levalbuterol inhalation solution when administered using other nebulizer systems have not been established.
Login To Your Free Account