FDA records indicate that there are no current recalls for this drug.
Are you a medical professional?
Trending Topics
Cancidas Recall
Get an alert when a recall is issued.
Questions & Answers
Side Effects & Adverse Reactions
There is currently no warning information available for this product. We apologize for any inconvenience.
Legal Issues
There is currently no legal information available for this drug.
FDA Safety Alerts
There are currently no FDA safety alerts available for this drug.
Manufacturer Warnings
There is currently no manufacturer warning information available for this drug.
FDA Labeling Changes
There are currently no FDA labeling changes available for this drug.
Uses
CANCIDAS® is indicated in adults and pediatric patients (3 months and older) for:
- Empirical therapy for presumed fungal infections in febrile, neutropenic patients
- Treatment of candidemia and the following Candida infections: intra-abdominal abscesses, peritonitis and pleural space infections. CANCIDAS has not been studied in endocarditis, osteomyelitis, and meningitis due to Candida.
- Treatment of esophageal candidiasis [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]
- Treatment of invasive aspergillosis in patients who are refractory to or intolerant of other therapies (e.g., amphotericin B, lipid formulations of amphotericin B, itraconazole). CANCIDAS has not been studied as initial therapy for invasive aspergillosis.
History
There is currently no drug history available for this drug.
Other Information
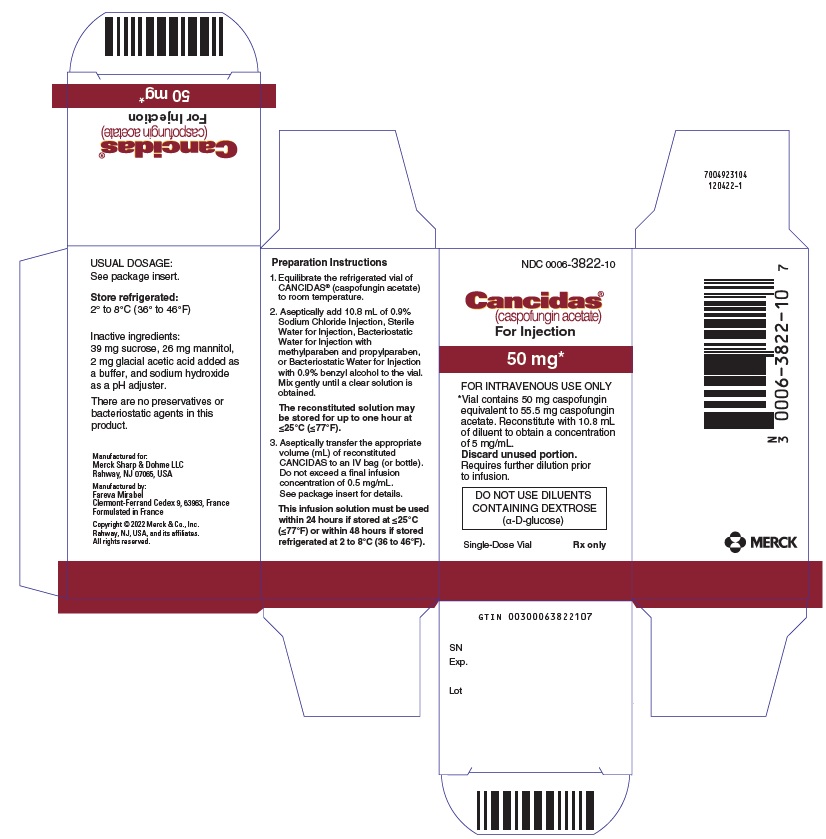
CANCIDAS is a sterile, lyophilized product for intravenous (IV) infusion that contains a semisynthetic lipopeptide (echinocandin) compound synthesized from a fermentation product of Glarea lozoyensis. CANCIDAS is an echinocandin that inhibits the synthesis of β (1,3)-D-glucan, an integral component of the fungal cell wall.
CANCIDAS (caspofungin acetate) is 1-[(4R,5S)-5-[(2-aminoethyl)amino]-N2-(10,12-dimethyl-1-oxotetradecyl)-4-hydroxy-L-ornithine]-5-[(3R)-3-hydroxy-L-ornithine] pneumocandin B0 diacetate (salt). CANCIDAS 50 mg also contains: 39 mg sucrose, 26 mg mannitol, glacial acetic acid, and sodium hydroxide. CANCIDAS 70 mg also contains 54 mg sucrose, 36 mg mannitol, glacial acetic acid, and sodium hydroxide. Caspofungin acetate is a hygroscopic, white to off-white powder. It is freely soluble in water and methanol, and slightly soluble in ethanol. The pH of a saturated aqueous solution of caspofungin acetate is approximately 6.6. The empirical formula is C52H88N10O15•2C2H4O2 and the formula weight is 1213.42. The structural formula is:

Sources
Cancidas Manufacturers
-
Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.
![Cancidas (Caspofungin Acetate) Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution [Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.]](/wp-content/themes/bootstrap/assets/img/loading2.gif)
Cancidas | Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.
![Cancidas (Caspofungin Acetate) Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution [Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.] Cancidas (Caspofungin Acetate) Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution [Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.]](/wp-content/themes/bootstrap/assets/img/loading2.gif)
2.1 Instructions for Use in All PatientsCANCIDAS should be administered by slow intravenous (IV) infusion over approximately 1 hour. CANCIDAS should not be administered by IV bolus administration.
Do not mix or co-infuse CANCIDAS with other medications, as there are no data available on the compatibility of CANCIDAS with other intravenous substances, additives, or medications. DO NOT USE DILUENTS CONTAINING DEXTROSE (α-D-GLUCOSE), as CANCIDAS is not stable in diluents containing dextrose.
2.2 Recommended Dosing in Adult Patients [≥18 years of age]The usual dose is 50 mg once daily (following a 70-mg loading dose for most indications). The safety and efficacy of a dose of 150 mg daily (range: 1 to 51 days; median: 14 days) have been studied in 100 adult patients with candidemia and other Candida infections. The efficacy of CANCIDAS at this higher dose was not significantly better than the efficacy of the 50-mg daily dose of CANCIDAS. The efficacy of doses higher than 50 mg daily in the other adult patients for whom CANCIDAS is indicated is not known [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
Empirical Therapy
A single 70-mg loading dose should be administered on Day 1, followed by 50 mg once daily thereafter. Duration of treatment should be based on the patient's clinical response. Empirical therapy should be continued until resolution of neutropenia. Patients found to have a fungal infection should be treated for a minimum of 14 days; treatment should continue for at least 7 days after both neutropenia and clinical symptoms are resolved. If the 50-mg dose is well tolerated but does not provide an adequate clinical response, the daily dose can be increased to 70 mg.
Candidemia and Other Candida Infections [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]
A single 70-mg loading dose should be administered on Day 1, followed by 50 mg once daily thereafter. Duration of treatment should be dictated by the patient's clinical and microbiological response. In general, antifungal therapy should continue for at least 14 days after the last positive culture. Patients who remain persistently neutropenic may warrant a longer course of therapy pending resolution of the neutropenia.
Esophageal Candidiasis
The dose is 50 mg once daily for 7 to 14 days after symptom resolution. A 70-mg loading dose has not been studied for this indication. Because of the risk of relapse of oropharyngeal candidiasis in patients with HIV infections, suppressive oral therapy could be considered [see Clinical Studies (14.3)].
Invasive Aspergillosis
A single 70-mg loading dose should be administered on Day 1, followed by 50 mg once daily thereafter. Duration of treatment should be based upon the severity of the patient's underlying disease, recovery from immunosuppression, and clinical response.
2.3 Recommended Dosing in Pediatric Patients [3 months to 17 years of age]For all indications, a single 70-mg/m2 loading dose should be administered on Day 1, followed by 50 mg/m2 once daily thereafter. The maximum loading dose and the daily maintenance dose should not exceed 70 mg, regardless of the patient's calculated dose. Dosing in pediatric patients (3 months to 17 years of age) should be based on the patient's body surface area (BSA) as calculated by the Mosteller Formula [see References (15)]:
Following calculation of the patient's BSA, the loading dose in milligrams should be calculated as BSA (m2) X 70 mg/m2. The maintenance dose in milligrams should be calculated as BSA (m2) X 50 mg/m2.
Duration of treatment should be individualized to the indication, as described for each indication in adults [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. If the 50-mg/m2 daily dose is well tolerated but does not provide an adequate clinical response, the daily dose can be increased to 70 mg/m2 daily (not to exceed 70 mg).
2.4 Patients with Hepatic ImpairmentAdult patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 5 to 6) do not need a dosage adjustment. For adult patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 7 to 9), CANCIDAS 35 mg once daily is recommended based upon pharmacokinetic data [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. However, where recommended, a 70-mg loading dose should still be administered on Day 1. There is no clinical experience in adult patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score >9) and in pediatric patients with any degree of hepatic impairment.
2.5 Patients Receiving Concomitant Inducers of Drug ClearanceAdult patients on rifampin should receive 70 mg of CANCIDAS once daily. Adult patients on nevirapine, efavirenz, carbamazepine, dexamethasone, or phenytoin may require an increase in dose to 70 mg of CANCIDAS once daily [see Drug Interactions (7)].
When CANCIDAS is co-administered to pediatric patients with inducers of drug clearance, such as rifampin, efavirenz, nevirapine, phenytoin, dexamethasone, or carbamazepine, a CANCIDAS dose of 70 mg/m2 once daily (not to exceed 70 mg) should be considered [see Drug Interactions (7)].
2.6 Preparation and Reconstitution for AdministrationDo not mix or co-infuse CANCIDAS with other medications, as there are no data available on the compatibility of CANCIDAS with other intravenous substances, additives, or medications. DO NOT USE DILUENTS CONTAINING DEXTROSE (α-D-GLUCOSE), as CANCIDAS is not stable in diluents containing dextrose.
Preparation of CANCIDAS for Infusion
Equilibrate the refrigerated vial of CANCIDAS to room temperature. Aseptically add 10.8 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, Sterile Water for Injection, Bacteriostatic Water for Injection with methylparaben and propylparaben, or Bacteriostatic Water for Injection with 0.9% benzyl alcohol to the vial.Each vial of CANCIDAS contains an intentional overfill of CANCIDAS. Thus, the drug concentration of the resulting solution is listed in Table 1 below.
Table 1: Information for Preparation of CANCIDAS CANCIDAS vial Total Drug Content
(including overfill) Reconstitution Volume
to be added Resulting Concentration
following Reconstitution 50 mg 54.6 mg 10.8 mL 5 mg/mL 70 mg 75.6 mg 10.8 mL 7 mg/mLThe white to off-white cake will dissolve completely. Mix gently until a clear solution is obtained. Visually inspect the reconstituted solution for particulate matter or discoloration during reconstitution and prior to infusion. Do not use if the solution is cloudy or has precipitated.
The reconstituted solution may be stored for up to one hour at ≤25°C (≤77°F).
CANCIDAS vials are for single use only; the remaining solution should be discarded.
C. Aseptically transfer the appropriate volume (mL) of reconstituted CANCIDAS to an IV bag (or bottle) containing 250 mL of 0.9%, 0.45%, or 0.225% Sodium Chloride Injection or Lactated Ringers Injection. Alternatively, the volume (mL) of reconstituted CANCIDAS can be added to a reduced volume of 0.9%, 0.45%, or 0.225% Sodium Chloride Injection or Lactated Ringers Injection, not to exceed a final concentration of 0.5 mg/mL.This infusion solution must be used within 24 hours if stored at ≤25°C (≤77°F) or within 48 hours if stored refrigerated at 2 to 8°C (36 to 46°F).
Special Considerations for Pediatric Patients >3 Months of Age
Follow the reconstitution procedures described above using either the 70-mg or 50-mg vial to create the reconstituted solution [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. From the reconstituted solution in the vial, remove the volume of drug equal to the calculated loading dose or calculated maintenance dose based on a concentration of 7 mg/mL (if reconstituted from the 70-mg vial) or a concentration of 5 mg/mL (if reconstituted from the 50-mg vial).
The choice of vial should be based on total milligram dose of drug to be administered to the pediatric patient. To help ensure accurate dosing, it is recommended for pediatric doses less than 50 mg that 50-mg vials (with a concentration of 5 mg/mL) be used if available. The 70-mg vial should be reserved for pediatric patients requiring doses greater than 50 mg.
The maximum loading dose and the daily maintenance dose should not exceed 70 mg, regardless of the patient's calculated dose.
-
Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.
Login To Your Free Account


![Cancidas (Caspofungin Acetate) Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution [Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=06dc6833-96c0-4a89-b975-0b84ab2b5a9e&name=caspofungin-01.jpg)