Nateglinide Recall
Get an alert when a recall is issued.
Questions & Answers
Side Effects & Adverse Reactions
FATALITIES ASSOCIATED WITH THE ADMINISTRATION OF SULFONAMIDES, ALTHOUGH RARE, HAVE OCCURRED DUE TO SEVERE REACTIONS, INCLUDING STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME, TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSIS, FULMINANT HEPATIC NECROSIS, AGRANULOCYTOSIS, APLASTIC ANEMIA AND OTHER BLOOD DYSCRASIAS.
SULFONAMIDES, INCLUDING SULFONAMIDE-CONTAINING PRODUCTS SUCH AS SULFAMETHOXAZOLE/TRIMETHOPRIM, SHOULD BE DISCONTINUED AT THE FIRST APPEARANCE OF SKIN RASH OR ANY SIGN OF ADVERSE REACTION. In rare instances, a skin rash may be followed by a more severe reaction, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, hepatic necrosis, and serious blood disorders (see PRECAUTIONS). Clinical signs, such as rash, sore throat, fever, arthralgia, pallor, purpura or jaundice may be early indications of serious reactions.
Cough, shortness of breath, and pulmonary infiltrates are hypersensitivity reactions of the respiratory tract that have been reported in association with sulfonamide treatment.
Thrombocytopenia
Sulfamethoxazole/Trimethoprim-induced thrombocytopenia may be an immune-mediated disorder. Severe cases of thrombocytopenia that are fatal or life threatening have been reported. Thrombocytopenia usually resolves within a week upon discontinuation of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim.
The sulfonamides should not be used for treatment of group alpha beta-hemolytic streptococcal infections. In an established infection, they will not eradicate the streptococcus and, therefore, will not prevent sequelae such as rheumatic fever.
Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
Legal Issues
There is currently no legal information available for this drug.
FDA Safety Alerts
There are currently no FDA safety alerts available for this drug.
Manufacturer Warnings
There is currently no manufacturer warning information available for this drug.
FDA Labeling Changes
There are currently no FDA labeling changes available for this drug.
Uses
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim tablets and other antibacterial drugs, sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim tablets should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Urinary Tract Infections
For the treatment of urinary tract infections due to susceptible strains of the following organisms: Escherichia coli, Klebsiella species, Enterobacter species, Morganella morganii, Proteus mirabilis and Proteus vulgaris. It is recommended that initial episodes of uncomplicated urinary tract infections be treated with a single effective antibacterial agent rather than the combination.
Acute Otitis Media
For the treatment of acute otitis media in pediatric patients due to susceptible strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenzae when in the judgment of the physician sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim offers some advantage over the use of other antimicrobial agents. To date, there are limited data on the safety of repeated use of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim in pediatric patients under two years of age. Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim is not indicated for prophylactic or prolonged administration in otitis media at any age.
Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis in Adults
For the treatment of acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis due to susceptible strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenzae when in the judgment of the physician sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim offers some advantage over the use of a single antimicrobial agent.
Shigellosis
For the treatment of enteritis caused by susceptible strains of Shigella flexneri and Shigella sonnei when antibacterial therapy is indicated.
Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia
For the treatment of documented Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia and for prophylaxis against Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in individuals who are immunosuppressed and considered to be at an increased risk of developing Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia.
Traveler’s Diarrhea in Adults
For the treatment of traveler’s diarrhea due to susceptible strains of enterotoxigenic E. coli.
History
There is currently no drug history available for this drug.
Other Information
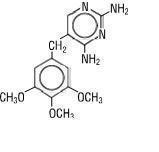
Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim is a synthetic antibacterial combination product available in 800 mg sulfamethoxazole and 160 mg trimethoprim Double Strength tablets and 400 mg sulfamethoxazole and 80 mg trimethoprim tablets for oral administration. Each Double Strength tablet contains 800 mg sulfamethoxazole and 160 mg trimethoprim plus magnesium stearate, pregelatinized starch and sodium starch glycolate. Each tablet contains 400 mg sulfamethoxazole and 80 mg trimethoprim plus magnesium stearate, pregelatinized starch, and sodium starch glycolate. Trimethoprim is 2, 4-diamino-5-(3,4,5 trimethoxybenzyl) pyrimidine: the molecular formula is C 14H 18N 4O 3. It is a white to light yellow, odorless, bitter compound with a molecular weight of 290.3 and the following structural formula:
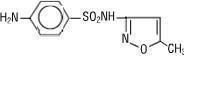
Sulfamethoxazole is N1-(5-methyl-3-isoxazolyl) sulfanilamide; the molecular formula is C10H11N3O3S. It is almost white, odorless, tasteless compound with a molecular weight of 253.28 and the following structural formula:
Sources