![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hcl) Tablet, Film Coated [Greenbrier International, Inc.] Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hcl) Tablet, Film Coated [Greenbrier International, Inc.]](/wp-content/themes/bootstrap/assets/img/loading2.gif)
If diarrhea occurs during therapy, this antibiotic should be discontinued. (See WARNING box).
Adults
Parenteral (IM or IV Administration):
Serious infections due to aerobic gram-positive cocci and the more susceptible anaerobes (NOT generally including Bacteroides fragilis, Peptococcus species and Clostridium species other than Clostridium perfringens):
600 to 1200 mg/day in 2, 3 or 4 equal doses.
More severe infections, particularly those due to proven or suspected Bacteroides fragilis, Peptococcus species, or Clostridium species
other than Clostridium perfringens:
1200 to 2700 mg/day in 2, 3 or 4 equal doses.
For more serious infections, these doses may have to be increased. In life-threatening situations due to either aerobes or anaerobes these doses may be increased. Doses of as much as 4800 mg daily have been given intravenously to adults. See Dilution and Infusion Rates section below.
Single IM injections of greater than 600 mg are not recommended.
Alternatively, drug may be administered in the form of a single rapid infusion of the first dose followed by continuous IV infusion as follows:
Neonates (less than 1 month)
15 to 20 mg/kg/day in three to four equal doses. The lower dosage may be adequate for small prematures.
Pediatric patients (1 month of age to 16 years)
Parenteral (IM or IV) administration: 20 to 40 mg/kg/day in 3 or 4 equal doses. The higher doses would be used for more severe infections. As an alternative to dosing on a body weight basis, pediatric patients may be dosed on the basis of square meters body surface: 350 mg/m2/day for serious infections and 450 mg/m2/day for more severe infections.
Parenteral therapy may be changed to clindamycin palmitate hydrochloride for oral solution or clindamycin hydrochloride capsules when the condition warrants and at the discretion of the physician.
In cases of B-hemolytic streptococcal infections, treatment should be continued for at least 10 days.
Dilution and Infusion Rates
Clindamycin phosphate must be diluted prior to I.V. administration. The concentration of clindamycin in diluent for infusion should not exceed 18 mg per mL. Infusion rates should not exceed 30 mg per minute.
The usual infusion dilutions and rates are as follows:
Administration of more than 1200 mg in a single 1-hour infusion is not recommended.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
Dilution and Compatibility
Physical and biological compatibility studies monitored for 24 hours at room temperature have demonstrated no inactivation or incompatibility with the use of clindamycin phosphate in IV solutions containing sodium chloride, glucose, calcium or potassium, and solutions containing vitamin B complex in concentrations usually used clinically. No incompatibility has been demonstrated with the antibiotics cephalothin, kanamycin, gentamicin, penicillin or carbenicillin.
The following drugs are physically incompatible with clindamycin phosphate: ampicillin sodium, phenytoin sodium, barbiturates, aminophylline, calcium gluconate, and magnesium sulfate.
The compatibility and duration of stability of drug admixtures will vary depending on concentration and other conditions.
Physico-Chemical Stability of Diluted Solutions of Clindamycin
Room temperature: 6, 9, and 12 mg/mL (equivalent to clindamycin base) in 5% Dextrose Injection, 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, or Lactated Ringer’s Injection in glass bottles or minibags, demonstrated physical and chemical stability for at least 16 days at 25°C. Also, 18 mg/mL (equivalent to clindamycin base) in 5% Dextrose Injection, in minibags, demonstrated physical and chemical stability for at least 16 days at 25°C.
Refrigeration: 6, 9 and 12 mg/mL (equivalent to clindamycin base) in 5% Dextrose Injection, 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, or Lactated Ringer’s Injection in glass bottles or minibags, demonstrated physical and chemical stability for at least 32 days at 4°C.
IMPORTANT: This chemical stability information in no way indicates that it would be acceptable practice to use this product well after the preparation time. Good professional practice suggests that compounded admixtures should be administered as soon after preparation as is feasible.
Frozen: 6, 9 and 12 mg/mL (equivalent to clindamycin base) in 5% Dextrose Injection, 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, or Lactated Ringer’s Injection in minibags demonstrated physical and chemical stability for at least eight weeks at -10°C.
Frozen solutions should be thawed at room temperature and not refrozen.
Caution: Do not use plastic containers in series connections. Such use could result in air embolism due to residual air being drawn
from the primary container before administration of the fluid from the secondary container is complete.


![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride) Capsule, Liquid Filled [H E B]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=cc019900-402c-433f-a2a3-70281ef996c9&name=diphenhydramine-25-mg-purple-softgel-1.jpg)
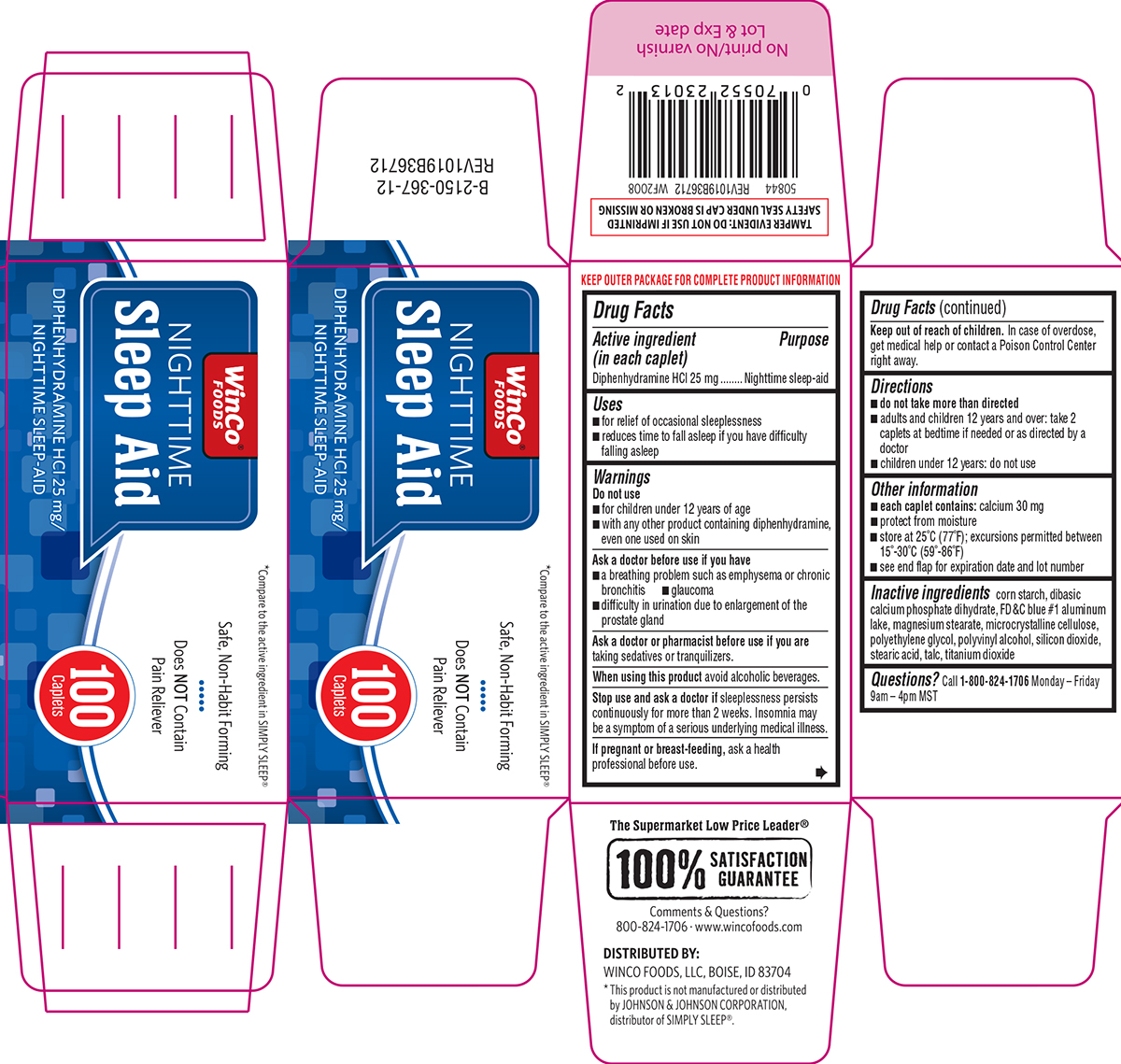
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride) Capsule, Liquid Filled [Winco Foods, Llc]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=07e4cd22-5a05-4976-b1d7-abd7ded41d3f&name=diphenhydramine-25-mg-purple-softgel-1.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride) Capsule, Liquid Filled [Freds Inc]](https://www.recallguide.org/wp-content/themes/bootstrap/assets/img/drug-image-placeholder.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Doxylamine Succinate) Tablet [Hyvee Inc]](http://www.recallguide.org/wp-content/themes/recallguide/assets/img/drug-image-placeholder.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hcl) Solution [Meijer Distribution Inc]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=5886353e-696c-4e55-b8c6-6667d56ff4a5&name=liqo2label.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hcl) Capsule, Liquid Filled [Hyvee Inc]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=9fad1dd8-6298-4dc5-8496-d6900a69cdd5&name=9fad1dd8-6298-4dc5-8496-d6900a69cdd5-01.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride) Tablet [Chain Drug Marketing Association]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=5fab9bd4-66d7-4356-a778-8900b2e270e2&name=F101902QCH_R2.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Doxylamine Succinate) Tablet [Cvs Pharmacy]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=05050b61-2417-48f0-9478-c39d6a341026&name=05050b61-2417-48f0-9478-c39d6a341026-01.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride) Tablet [H E B]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=b72c47a3-cae3-4b98-ae85-e1313b6fd501&name=b72c47a3-cae3-4b98-ae85-e1313b6fd501-01.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride) Tablet [Kroger Company]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=7faee1af-c126-4786-8e6d-6c07490259fd&name=image-01.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hcl) Tablet [Western Family Foods, Inc.]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=cc944809-2609-41bd-a00e-7a96cfc5b248&name=diphenhydramine-hcl-25-mg-1.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hcl) Capsule [Western Family Foods, Inc.]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=b5731789-874d-4dd8-a92a-1703eef5cef3&name=diphenhydramine-hcl-50-mg-softgel-1.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Doxylamine Succinate) Tablet [Great Lakes Wholesale, Marketing, & Sales, Inc.]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=b0df082a-838f-4556-8399-dd8229c5974a&name=Label1.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hcl) Capsule [Valu Merchandisers Company (Best Choice)]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=6ef61442-cb62-4157-a971-0f5b826c9c3f&name=diphenhydramine-hcl-50-mg-softgels-1.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hcl) Tablet [Supervalu (Equaline)]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=e3daf907-4836-4f37-9b78-a16f1a3dbec6&name=diphenhydramine-hcl-25-mg-blue-caplets-1.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride 50 Mg) Capsule, Liquid Filled [Puravation Pharmaceuticals Inc]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=4400053d-e06f-44f0-9842-835438e2461a&name=NightTimeSleepAid-Diphen50mg32ct.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hcl) Capsule [Good Sense (Geiss, Destin & Dunn, Inc.)]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=1148ac73-c6c8-4d54-a940-2a7667cf09de&name=diphenhydramine-hcl-50-mg-softgels-1.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hcl) Capsule [Equaline (Supervalu)]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=0cf43545-f741-44e6-9a81-91d20a3c2f87&name=diphenhydramine-hcl-50-mg-1.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hcl) Capsule [Supervalu Inc.]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=6c9b7576-428a-4884-8331-bb312c9046bd&name=equaline-44-367-1.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hcl) Tablet, Film Coated [Woonsocket Prescription Center,incorporated]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=de254786-b20e-4739-9c50-e640400b50a7&name=ae80240a-2f59-425e-a8ed-68201efeeb16-05.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hcl) Tablet, Film Coated [Target Corporation]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=2bef39c3-3c1b-4a2d-a8d2-befe4efd2c8c&name=nighttime-sleep-aid-1.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hcl) Tablet, Film Coated [Walgreen Co.]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=f93a1f1f-2233-4338-9643-1ba48bd000bc&name=exchange-select-44-375-1.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Doxylamine Succinate) Tablet [Wal-mart Stores Inc]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=79925559-25ad-4ecc-8e82-a7b45229ca34&name=hydrocortisone-lt-02.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hcl) Tablet [The Kroger Co.]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=365ee0e0-a15c-4ae0-93ad-45379a6a24ba&name=diphenhydramine-25-mg-sleep-aid-1.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hcl) Tablet [Equate (Walmart Stores, Inc.)]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=4fe2013a-bd8e-481b-8068-780d6b7d29f3&name=diphenhydramine-hcl-25mg-blue-caplet-1.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride) Capsule, Liquid Filled [H E B]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=3047ade9-34d0-4333-8a89-aaafaf69f40e&name=diphenhydramine-25-mg-purple-softgel-1.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hcl) Capsule, Liquid Filled [Woonsocket Prescription Center,incorporated]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=fe402eec-1314-4c7e-820c-b4b4edcd4cc2&name=cvs-44-293-delisted-1.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hcl) Liquid [H E B]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=d93ff75d-9cdb-476c-bb65-eabeefb91a34&name=image-01.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride) Capsule, Liquid Filled [Our Family (Nash Finch Company)]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=7023f07b-b1d5-43a3-b860-238f0b8a5636&name=diphenhydramine-25mg-purple-softgel-1.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride) Capsule, Liquid Filled [Safeway, Inc.]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=c10ddb43-2c44-49f3-bfdc-d47a628b2c08&name=diphenhydramine-hcl-25-mg-purpule-softgel-1.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride) Liquid [Fred’s, Inc.]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=5089fd55-d51b-4bc9-aa05-cbc175c40e04&name=nighttime-01.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Doxylamine Succinate) Tablet [Woonsocket Prescription Center,incorporated]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=ae0ec49b-f227-4127-818f-1afd50e78aad&name=SMirapharm.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride) Capsule, Liquid Filled [Best Choice (Valu Merchandisers Company)]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=f862dd3a-c35c-4152-b225-e765adba4b72&name=diphenhydramine-hcl-50-mg-softgel-1.jpg)
![Nighttime Sleep Aid (Doxylamine Succinate) Tablet [Kroger Company]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=c5f276c2-f56c-43eb-b9bb-21f323d7f449&name=c5f276c2-f56c-43eb-b9bb-21f323d7f449-01.jpg)