Propoxyphene Recall
Get an alert when a recall is issued.
Questions & Answers
Side Effects & Adverse Reactions
WARNINGS
Risk of Overdose
There have been numerous cases of accidental and intentional overdose with propoxyphene products either alone or in combination with other CNS depressants, including alcohol. Fatalities within the first hour of overdosage are not uncommon. Many of the propoxyphene-related deaths have occurred in patients with previous histories of emotional disturbances or suicidal ideation/attempts and/or concomitant administration of sedatives, tranquilizers, muscle relaxants, antidepressants or other CNS-depressant drugs. Do not prescribe propoxyphene for patients who are suicidal or have a history of suicidal ideation.
Respiratory Depression
Respiratory depression is the chief hazard from all opioid agonist preparations. Respiratory depression occurs most frequently in elderly or debilitated patients, usually following large initial doses in non-tolerant patients, or when opioids are given in conjunction with other agents that depress respiration. Propoxyphene should be used with extreme caution in patients with significant chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or cor pulmonale, and in patients having substantially decreased respiratory reserve, hypoxia, hypercapnia, or preexisting respiratory depression. In such patients, even usual therapeutic doses of propoxyphene may decrease respiratory drive to the point of apnea. In these patients alternative non-opioid analgesics should be considered and opioids should be employed only under careful medical supervision at the lowest effective dose.
Hypotensive Effect
Propoxyphene, like all opioid analgesics, may cause severe hypotension in an individual whose ability to maintain blood pressure has been compromised by a depleted blood volume, or after concurrent administration with drugs such as phenothiazines or other agents which compromise vasomotor tone. Propoxyphene may produce orthostatic hypotension in ambulatory patients. Propoxyphene, like all opioid analgesics, should be administered with caution to patients in circulatory shock, since vasodilatation produced by the drug may further reduce cardiac output and blood pressure.
Head Injury and Increased Intracranial Pressure
The respiratory depressant effects of narcotics and their capacity to elevate cerebrospinal fluid pressure may be markedly exaggerated in the presence of head injury, other intracranial lesions or a preexisting increase in intracranial pressure. Furthermore, narcotics produce adverse reactions which may obscure the clinical course of patients with head injuries.
Drug Interactions
The concomitant use of propoxyphene and CNS depressants, including alcohol, can result in potentially serious adverse events including death. Because of its added depressant effects, propoxyphene should be prescribed with caution for those patients whose medical condition requires the concomitant administration of sedatives, tranquilizers, muscle relaxants, antidepressants or other CNS-depressant drugs.
Usage in Ambulatory Patients
Propoxyphene may impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks, such as driving a car or operating machinery. The patient should be cautioned accordingly.
Use with Alcohol
Patients should be cautioned about the concomitant use of propoxyphene products and alcohol because of potentially serious CNS-additive effects of these agents that can lead to death.
Legal Issues
There is currently no legal information available for this drug.
FDA Safety Alerts
There are currently no FDA safety alerts available for this drug.
Manufacturer Warnings
There is currently no manufacturer warning information available for this drug.
FDA Labeling Changes
There are currently no FDA labeling changes available for this drug.
Uses
INDICATION
Propoxyphene hydrochloride capsules are indicated for the relief of mild to moderate pain.
History
There is currently no drug history available for this drug.
Other Information
DESCRIPTION
Propoxyphene hydrochloride, USP is an odorless, white crystalline powder with a bitter taste. It is freely soluble in water. Chemically, it is (2S,3R)-(+)-4-(Dimethylamino)-3-methyl-1,2-diphenyl-2-butanol propionate (ester) hydrochloride, which can be represented by the accompanying structural formula. Its molecular formula is C22H29NO2∙HCl and its molecular weight is 375.93.
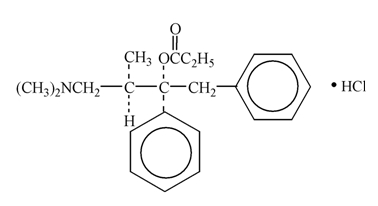
Each capsule contains 65 mg (172.9 μmol) propoxyphene hydrochloride. It also contains the following inactive ingredients: anhydrous lactose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, pregelatinized starch and sodium lauryl sulfate. The empty hard-shell hypromellose capsule shells contain carnauba wax, carrageenan, hypromellose, potassium chloride, synthetic red iron oxide and titanium dioxide. In addition, the imprinting ink contains black iron oxide, potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol, shellac and strong ammonia solution.
Sources