FDA records indicate that there are no current recalls for this drug.
Are you a medical professional?
Trending Topics
Qsymia Recall
Get an alert when a recall is issued.
Questions & Answers
Side Effects & Adverse Reactions
There is currently no warning information available for this product. We apologize for any inconvenience.
Legal Issues
There is currently no legal information available for this drug.
FDA Safety Alerts
There are currently no FDA safety alerts available for this drug.
Manufacturer Warnings
There is currently no manufacturer warning information available for this drug.
FDA Labeling Changes
There are currently no FDA labeling changes available for this drug.
Uses
Qsymia is indicated as an adjunct to a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity for chronic weight management in adult patients with an initial body mass index (BMI) of
- 30 kg/m2 or greater (obese), or
- 27 kg/m2 or greater (overweight) in the presence of at least one weight related comorbidity such as hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, or dyslipidemia
Limitations of Use
- The effect of Qsymia on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality has not been established.
- The safety and effectiveness of Qsymia in combination with other products intended for weight loss, including prescription and over-the-counter drugs and herbal preparations have not been established.
History
There is currently no drug history available for this drug.
Other Information
Qsymia capsule is a combination oral product comprised of immediate-release phentermine hydrochloride (expressed as the weight of the free base) and extended-release topiramate. Qsymia contains phentermine hydrochloride, a sympathomimetic amine anorectic, and topiramate, a sulfamate-substituted monosaccharide related to fructose antiepileptic drug.
Phentermine Hydrochloride
The chemical name of phentermine hydrochloride is α,α-dimethylphenethylamine hydrochloride. The molecular formula is C10H15N • HCl and its molecular weight is 185.7 (hydrochloride salt) or 149.2 (free base). Phentermine hydrochloride is a white, odorless, hygroscopic, crystalline powder that is soluble in water, methanol, and ethanol. Its structural formula is:

Topiramate
Topiramate is 2,3:4,5-di-O-isopropylidene-β-D-fructopyranose sulfamate. The molecular formula is C12H21NO8S and its molecular weight is 339.4. Topiramate is a white to off-white crystalline powder with a bitter taste. It is freely soluble in methanol and acetone, sparingly soluble in pH 9 to pH 12 aqueous solutions and slightly soluble in pH 1 to pH 8 aqueous solutions. Its structural formula is:

Qsymia
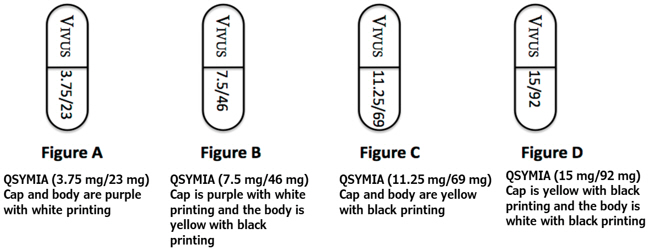
Qsymia is available in four dosage strengths:
- Qsymia 3.75 mg/23 mg (phentermine 3.75 mg and topiramate 23 mg extended-release) capsules;
- Qsymia 7.5 mg/46 mg (phentermine 7.5 mg and topiramate 46 mg extended-release) capsules;
- Qsymia 11.25 mg/69 mg (phentermine 11.25 mg and topiramate 69 mg extended-release) capsules;
- Qsymia 15 mg/92 mg (phentermine 15 mg and topiramate 92 mg extended-release) capsules.
Each capsule contains the following inactive ingredients: methylcellulose, sucrose, starch, microcrystalline cellulose, ethylcellulose, povidone, gelatin, talc, titanium dioxide, FD&C Blue #1, FD&C Red #3, FD&C Yellow #5 and #6, and pharmaceutical black and white inks.
Sources
Qsymia Manufacturers
-
Vivus, Inc.
![Qsymia (Phentermine And Topiramate) Capsule, Extended Release [Vivus, Inc.]](/wp-content/themes/bootstrap/assets/img/loading2.gif)
Qsymia | Vivus, Inc.
![Qsymia (Phentermine And Topiramate) Capsule, Extended Release [Vivus, Inc.] Qsymia (Phentermine And Topiramate) Capsule, Extended Release [Vivus, Inc.]](/wp-content/themes/bootstrap/assets/img/loading2.gif)
2.1 General Dosing and AdministrationDetermine the patient's BMI. BMI is calculated by dividing weight (in kilograms) by height (in meters) squared. A BMI conversion chart (Table 1) based on height [inches (in) or centimeters (cm)] and weight [pounds (lb) or kilograms (kg)] is provided below.
Table 1. BMI Conversion ChartIn adults with an initial BMI of 30 kg/m2 or greater or 27 kg/m2 or greater when accompanied by weight-related co-morbidities such as hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, or dyslipidemia prescribe Qsymia as follows:
Take Qsymia once daily in the morning with or without food. Avoid dosing with Qsymia in the evening due to the possibility of insomnia. Start treatment with Qsymia 3.75 mg/23 mg (phentermine 3.75 mg/topiramate 23 mg extended-release) daily for 14 days; after 14 days increase to the recommended dose of Qsymia 7.5 mg/46 mg (phentermine 7.5 mg/topiramate 46 mg extended-release) once daily. Evaluate weight loss after 12 weeks of treatment with Qsymia 7.5 mg/46 mg.
If a patient has not lost at least 3% of baseline body weight on Qsymia 7.5 mg/46 mg, discontinue Qsymia or escalate the dose, as it is unlikely that the patient will achieve and sustain clinically meaningful weight loss at the Qsymia 7.5 mg/46 mg dose.
To escalate the dose: Increase to Qsymia 11.25 mg/69 mg (phentermine 11.25 mg/topiramate 69 mg extended-release) daily for 14 days; followed by dosing Qsymia 15 mg/92 mg (phentermine 15 mg/topiramate 92 mg extended-release) once daily. Evaluate weight loss following dose escalation to Qsymia 15 mg/92 mg after an additional 12 weeks of treatment.
If a patient has not lost at least 5% of baseline body weight on Qsymia 15 mg/92 mg, discontinue Qsymia as directed, as it is unlikely that the patient will achieve and sustain clinically meaningful weight loss with continued treatment. Qsymia 3.75 mg/23 mg and Qsymia 11.25 mg/69 mg are for titration purposes only.Discontinuing Qsymia
Discontinue Qsymia 15 mg/92 mg gradually by taking a dose every other day for at least 1 week prior to stopping treatment altogether, due to the possibility of precipitating a seizure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]. 2.2 Dosing in Patients with Renal ImpairmentIn patients with moderate (creatinine clearance [CrCl] greater than or equal to 30 and less than 50 mL/min) or severe (CrCl less than 30 mL/min) renal impairment dosing should not exceed Qsymia 7.5 mg/46 mg once daily. Renal impairment is determined by calculating CrCl using the Cockcroft-Gault equation with actual body weight [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.3 Dosing in Patients with Hepatic ImpairmentIn patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 7 - 9), dosing should not exceed Qsymia 7.5 mg/46 mg once daily [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Login To Your Free Account