Zafirlukast Recall
Get an alert when a recall is issued.
Questions & Answers
Side Effects & Adverse Reactions
Hepatotoxicity:
Cases of life-threatening hepatic failure have been reported in patients treated with zafirlukast. Cases of liver injury without other attributable cause have been reported from post-marketing adverse event surveillance of patients who have received the recommended dose of zafirlukast (40 mg/day). In most, but not all post-marketing reports, the patient’s symptoms abated and the liver enzymes returned to normal or near normal after stopping zafirlukast. In rare cases, patients have either presented with fulminant hepatitis or progressed to hepatic failure, liver transplantation and death. In extremely rare post-marketing cases, no clinical symptoms or signs suggestive of liver dysfunction were reported to precede the latter observations.
Physicians may consider the value of liver function testing. Periodic serum transaminase testing has not proven to prevent serious injury but it is generally believed that early detection of drug-induced hepatic injury along with immediate withdrawal of the suspect drug enhances the likelihood for recovery.
Patients should be advised to be alert for signs and symptoms of liver dysfunction (eg, right upper quadrant abdominal pain, nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, jaundice, flu-like symptoms, and anorexia) and to contact their physician immediately if they occur. Ongoing clinical assessment of patients should govern physician interventions, including diagnostic evaluations and treatment.
If liver dysfunction is suspected based upon clinical signs or symptoms (eg, right upper quadrant abdominal pain, nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, jaundice, flu-like symptoms, anorexia, and enlarged liver), zafirlukast should be discontinued. Liver function tests, in particular serum ALT, should be measured immediately and the patient managed accordingly. If liver function tests are consistent with hepatic dysfunction, zafirlukast therapy should not be resumed. Patients in whom zafirlukast was withdrawn because of hepatic dysfunction where no other attributable cause is identified should not be re-exposed to zafirlukast (see PRECAUTIONS, Information for Patients and ADVERSE REACTIONS).
Bronchospasm:
Zafirlukast tablets are not indicated for use in the reversal of bronchospasm in acute asthma attacks, including status asthmaticus. Therapy with zafirlukast can be continued during acute exacerbations of asthma.
Concomitant Warfarin Administration:
Coadministration of zafirlukast with warfarin results in a clinically significant increase in prothrombin time (PT). Patients on oral warfarin anticoagulant therapy and zafirlukast should have their prothrombin times monitored closely and anticoagulant dose adjusted accordingly (see PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions).
Legal Issues
There is currently no legal information available for this drug.
FDA Safety Alerts
There are currently no FDA safety alerts available for this drug.
Manufacturer Warnings
There is currently no manufacturer warning information available for this drug.
FDA Labeling Changes
There are currently no FDA labeling changes available for this drug.
Uses
Zafirlukast tablets are indicated for the prophylaxis and chronic treatment of asthma in adults and children 5 years of age and older.
History
There is currently no drug history available for this drug.
Other Information
Zafirlukast is a synthetic, selective peptide leukotriene receptor antagonist (LTRA), with the chemical name 4-(5-cyclopentyloxy-carbonylamino-1-methyl-indol-3-ylmethyl)-3-methoxy-N-o-tolylsulfonylbenzamide. The molecular weight of zafirlukast is 575.7 and the structural formula is:
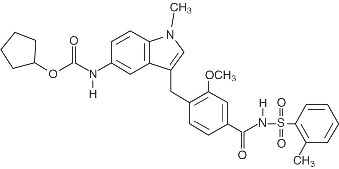
The molecular formula is: C31H33N3O6S
Zafirlukast, white to pale yellow coloured powder, freely soluble in tetrahydrofuran, and dimethylsulfoxide and practically insoluble in water.
Zafirlukast is supplied as 10 and 20 mg tablets for oral administration.
Inactive ingredients: Film coated tablets containing hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol 400, sodium starch glycolate (Type-A) and titanium dioxide. .
Sources